Agile Software Methodology
July 17, 2021
Agile Software Methodology 
-
Agile Software Methodology

AGILE
- 4 values & 12 principles
Benefits of using AGILE
- Little bit value by giving the working software. As you know waterfall, we know only at the end.
Challenges
- Less documentation, so other support team might feel difficult to understand.
Differnt Methodologies
Scrum Overview
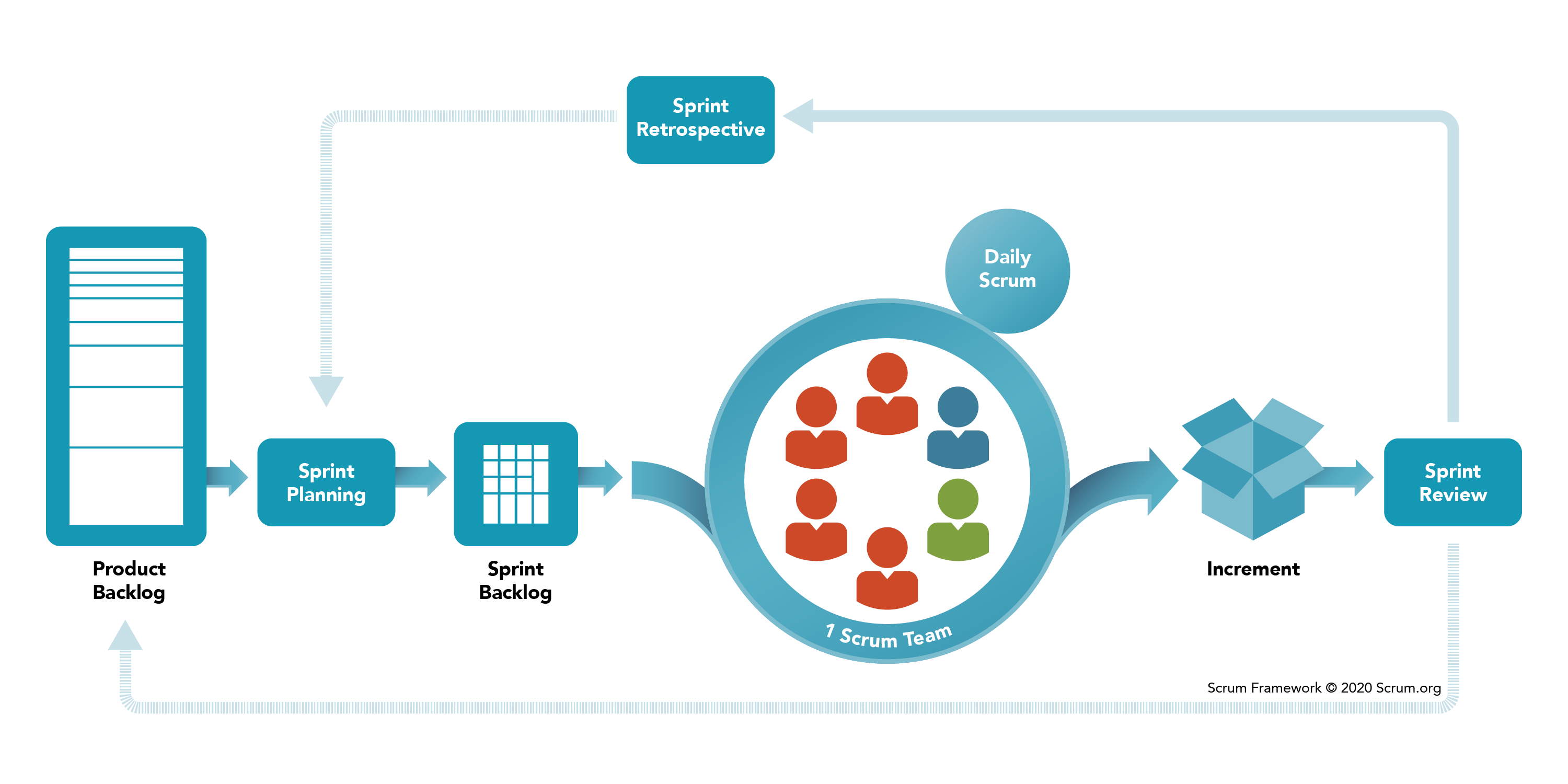
- Inspect and adapt
- Transparency (Meeting and roles are public)
- Sprint - Time box - Planning
- Scrum Values : Openness, Focus, Courage, Commitment, Respect
- Sprint : Usually it is about 1-4 weeks. In this Sprint planning, daily standups, sprint review and retrospective all happen inside of sprint.
Roles
- Product Owner : features. Business translate to wrok units like business analyst. Mangerial stuff between business and project. Prioritise the user stories, refine them. Focus on MVP (Minimum viable product). A team should have dedicated product owner, so that he is available.
- Scrum Master : servent leader, maintains values. Asks 3 Q’s yesterday, today and any challenges. Takes review and retrospection. In Retrospection they ask 3 Q’s again, what went well ?, What didnt go well ?, what to improve ? TO get the overall team sentiment.
- Development team : BA, architect, QA, Devs. self-organising, cross functional. Internal assign roles such as BA or product specialist, where he check bottle-necks. Create stories.
Methodology
- Daily Standup : discuss about Yesterday, Today and any challenges. This is for all not just for the project manager, Be crisp as others are waiting for thier turn.
- Sprint Planning : O/P —> Sprint Backlogs (tasks or stories) they are going to work in two-wfeeks. Prioritise the stories and customers. Alloting story points.
- Sprint Review (Last day): To share outcomes (Overall backlogs) of sprint with external stakeholders. Around 1-2 hours. Attended by entire team + product owner + customer.
- Sprint Retrospective : What did team do well ? Went wrong ? Challenges. Improvements ? Gathering data - insights. O/P - How to improve, what to do be done in the next sprint. You can also do LUNCH RETRO, potray pictorial (shark-risk, WIND-improved, island -safe)
- Backlog grooming : is reprioritizing the user stories, keeping in view of the current picture and the future.
Scrum terms and artifacts
- User Stories : Who ? What ? Why ?
- 3 C’s = Card; Conversation; Confirmation
- Acceptance criteria
-
INVEST ACRONYM
- Independent
- Negotiable
- Valuable
- Estimatable
- Small - finish in few days
- Testable - can be tested
- Product Backlog - prioritize the user stories; monitored by the product owner.
- Sprint Backlog - user stories are added to the upcoming sprint.
- Working Agreement - rules, expectations and procedures that govern how team works. Since no dictatorship, it should be collabrative. Updated and changed as per needs.
- Defination of Ready - when user stories contains enough details to be worked - ACTIONABLE - WHO WHAT WHY.
-
Defination of done - Accesible by everyone, common agreement. (Not individual to a story)
- Include acceptance criteria
- Tested
- Code Review, Peer testing
- User story testable by product owner
- DONE DONE - entirely finished and ready to go live.
Estimating in Agile
- Use the elicited information, past experiences, documentation.
- Use relative estimate rather than absolute estimate.
- Highlight complex and high risk tasks
- Common techniques - BUS (Big : Uncertain : Small), TShirt sizes, Fibonnacci
Agile vs Traditional
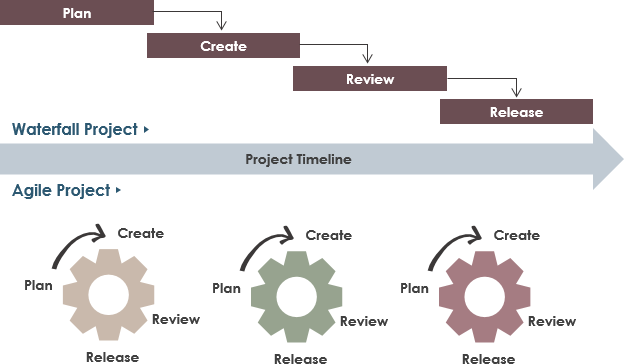
- Vertical vs Horizontal product imcrementes
- e.g v1.4,1.5 keep on incrementing. Product increment is a vertical slice that version.
Scrum Methodology - deeper
Team Velocity
- avergage number of story points that the team can finish. Estimeated velocity is 12 which is commited, but completed around 10 pts then the team velocity is 10.
Burndown chart
- Work completed during the various sprints. (X,Y) -> (Sprints, Story pts)

Burn Up chart
-
Helps in poiting some more changes when work was added or changed.

-
Using non-fibonacci sequences also similar by assigning relative numbers to TShirt sizes, but keep in mind there is chance that more story points may also indicate that easy specs are getting finsihed.
Kanban Methodology - Stop starting, Start finishing
4 Basic principles of Kanban
- Start with what you know
- Incremental changes
- Respect current proces, roles, responsibilities
- Encourage acts of leadership at all levels.
Kanban board
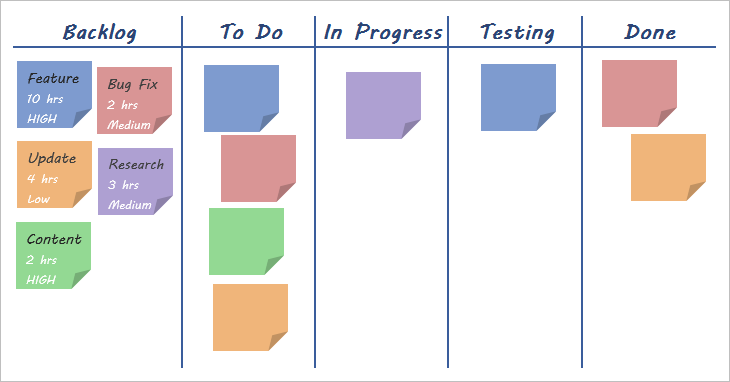
- Some companies use touch screen board to move from INPROGRESS - > DONE, to get the physical feeling of accomplishing task.
6 General principles of Kanban
- Visualize the workflow
- Limit WIP - work in progress
- Manage flow
- Make policies explicit - others know how things work
- Implement feedback loops - retrospection
- Collabrate for improvement, evolve experimentally - discuss
Kanban key metrics
- Lead time
- Cycle time - focus on one ad finish it, keep it short
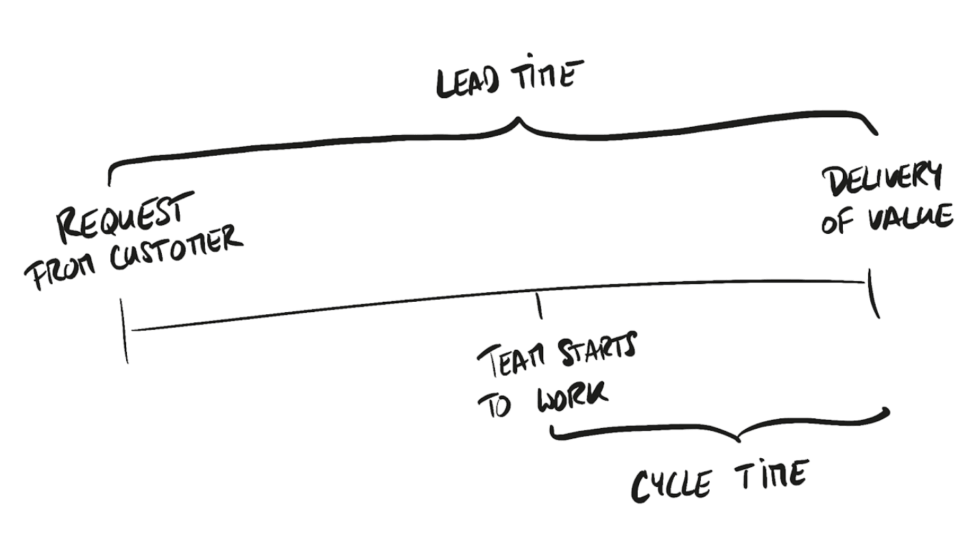
- Check trello or JIRA boards, some new features such as setting column limits.
- Boards status can be changed based on the project needs - Can also add new status Future tasks, Now Tasks
- Swimlanes help in prioritizing the tasks or group based on similarities.
Quick steps to get started
- Step 1 : Visualize your work - know the tip of iceberg, try priortizing
- Step 2: Limit WIP - Focus on 1 task than task switching, reduce cycle time and finish tasks. Keep things flowing, eg. traffic flow.
- Step 3 : Adapt, monitor and improve
Scrumban
Overview
- Visualize workflow using Kanban board
- Utilize daily scrum
- Work is pulled, rather than assigned
- Strict WIP limits
- Project team roles not specified
- Specialized team members - not cross-functional like Agile
Debate : whether to have timebox or fluidity of board
-
Continuous flow
- no timeboxes, pull items into doing tasks based on capacity
- Based on Status limits, if TODO items less than 5 then add more.
- Key metrics to measure are Lead and Cycle time.
TimeBox
- Sprint (1-4 weeks), which includes iteration - reviews - retrospection
- Use Backlogs -> Ready state (Flag items) to organize work items to say when they are ready to work
- Metrics include lead and cycle time or burn down charts
- Triage and Feature freeze : focuses the team’s energy on finishing the critical tasks
- Target audience - Who are bit mature in Agile or new organization or wants Scrum + Fluid movement, simply it is best practices of Scrum + Kanban